MYTHS OF THE LABYRINTH
Uncovering the myths of the Labyrinth and the Minotaur
6-minute read
By Andrew Shapland
Sir Arthur Evans Curator of Bronze Age and Classical Greece
Throughout history we have been fascinated by the stories and symbolism of the Cretan Labyrinth and the Minotaur that was said to lurk within.
Here, Andrew Shapland, curator of the Ashmolean's spring 2023 exhibition, uncovers more.
THE LABYRINTH IN MYTH AND HISTORY
In Greek myth, the Minotaur was a monster with the head of a bull and the body of a man who was imprisoned in a dark underground labyrinth at Knossos on the Aegean island of Crete.

Inside the Labyrinth exhibition showing the marble Minotaur statue © Ashmolean. Photo Ellie Atkins
The Labyrinth was an ingenious maze commissioned by King Minos and designed by the architect Daedalus.
In order to escape the maze after killing the Minotaur, Theseus needed a ball of thread, given to him by the princess Ariadne. Or at least that is the most commonly accepted story – digging deeper into the myth reveals a multitude of contradictory versions. Myths are continually reworked and retold, and that of the Labyrinth is no exception.
Knossos, on the island of Crete, is mentioned in the earliest work of Greek literature, Homer’s Iliad, which was composed some time before 700 BCE. Intriguingly, Homer tells us that Daedalus built a dancing floor for Ariadne at Knossos, but doesn’t mention the Labyrinth.
Herodotus, the earliest Greek historian, describes an impressive building called a labyrinth, but locates it in Egypt, at a city called Crocodilopolis.
Only later did authors locate the Labyrinth at Knossos.
Writing several hundred years later, the Roman historian Pliny the Elder lists a number of different labyrinths, suggesting that the Egyptian building had inspired Daedalus to build the one in Crete. But of this Cretan Labyrinth, Pliny says, nothing remained.
At the same time as these different accounts of the Labyrinth were being written down, artists were producing a variety of depictions of the myth. Greek vases frequently show Theseus killing the Minotaur with a sword.
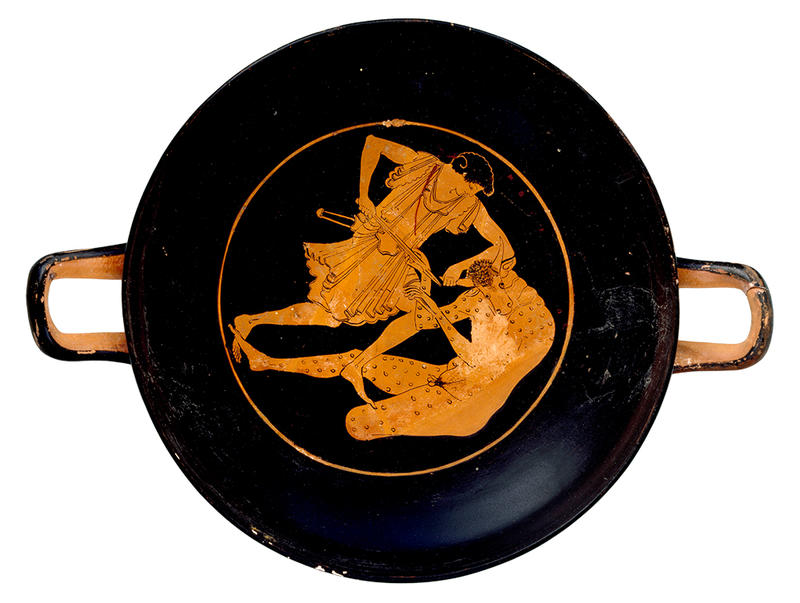

Attic red-figure cup, c. 500 BCE, Ashmolean AN1896-1908.G.261 © Ashmolean Museum
The coins of Knossos were decorated with a symbol of the city: a labyrinth design which sometimes had a Minotaur at the centre. This design, unlike most literary descriptions, has a single path into the centre. It appears more like a bird’s eye view of a building, and one in which it is impossible to get lost.

Hellenistic coin from Knossos, 300-200 BCE, showing the labyrinthine design HCR 4579
Knossos was an important Cretan city in the Greek and Roman period. When the Roman conquest of Crete began in 69 BCE, its citizens resisted. As a result the rival city of Gortyn, 60 km south of Knossos, became the Roman provincial capital. New civic buildings were required, and the stone for these was quarried out of a nearby hillside. This left a network of underground passages going deep underground.
From this period onwards, authors start to confuse Knossos and Gortyn, and the location of the Labyrinth started to shift. The Roman poet, Catullus for instance, refers to the home of King Minos as ‘Gortynian’. A later Byzantine author, Ioannes Malalas, described the labyrinth as a cave near Gortyn.

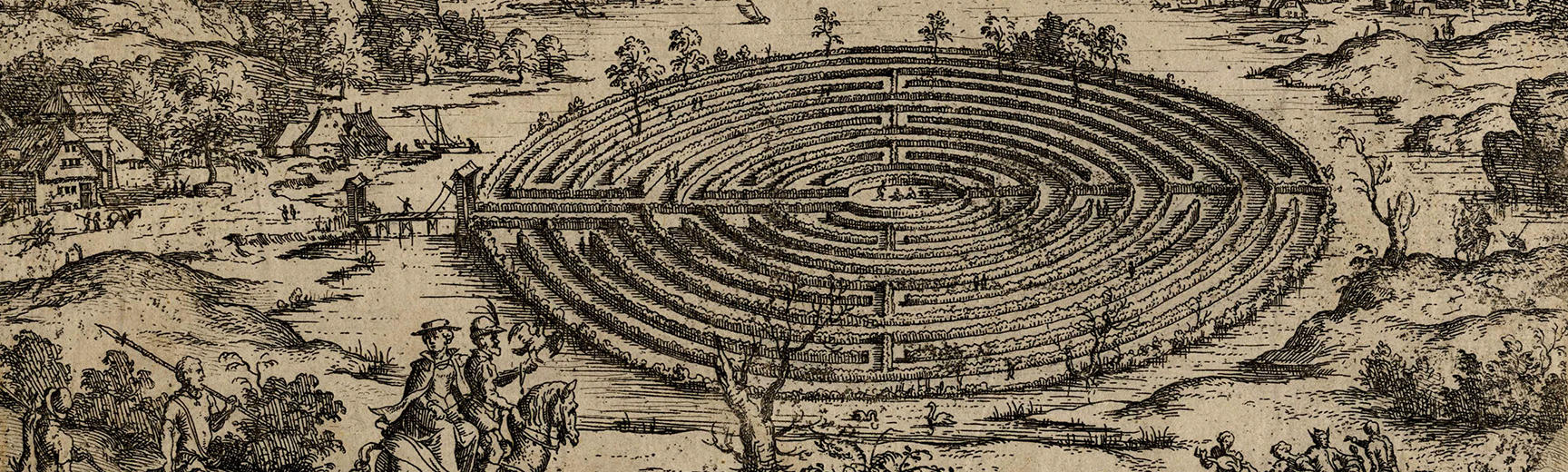
The Cretan Labyrinth by Hieronymus Cock after Matthijs Cock, c.1558 © Ashmolean Museum. The Labyrinth in this landscape print derived from contemporary 16th-century garden design
LOOKING FOR THE LABYRINTH
The Renaissance renewed interest in Greece and its myths, resulting in a search for the real labyrinth.
The Florentine priest, Cristoforo Buondelmonti, first visited Crete in 1415 and explored both Knossos and Gortyn. By this time there was little to see at Knossos – it had been abandoned following an earthquake in the 8th century CE – and certainly nothing that resembled the Labyrinth.
Buondelmonti described the underground passages near Gortyn, and although he recognised it as a quarry, his map of the island shows the Labyrinth as a cave in the middle of the island. Other authors who did not visit Crete tended to place the Labyrinth near Knossos.
Wolfgang Lazius, the 16th-century Austrian cartographer, for instance, uses the labyrinth design found on coins of the city. His Minotaur, incidentally, has the bearded face of a man and the horns and body of a bull.

Detail of map showing the Cretan maze and Minotaur from Commen: Rerum Graecarum Libri II by Wolfgang Lazius, 1558, Bodleian Libraries K 6.8 Art
The debate over the location of the true labyrinth continued for several hundred years.
In the 19th century, Captain Thomas Spratt visited the caves at Gortyn while surveying Crete for a new map of the island for the British Admiralty. He described them as 'unquestionably a real labyrinth, such as the ancients understood by that term' and wondered if King Minos had kept Athenians prisoners there.
Robert Pashley, the 19th-century traveller, meanwhile regarded the Labyrinth as 'a work of the imagination' but kept faith with Knossos, despite the fact that it had 'dwindled down into this miserable hamlet'.
The location of Knossos had never been forgotten since coins of the city continued to be found there. The problem was that there was nothing to see there for those going in search of the Labyrinth.
The argument was finally resolved in 1878 by a local businessman named, appropriately enough, Minos Kalokairinos.

Minos Kalokairinos, 1843-1907, local Cretan businessman and original excavator at Knossos © Historical Museum of Crete
He had been inspired to dig at Knossos by the excavations of Heinrich Schliemann at Troy and Mycenae. There Schliemann had found archaeological treasures which seemed to link these places with their mythical past.
Digging on an area to the south of the Greek and Roman city, on the bare Kephala hill, Kalokairinos soon found the remains of a building with curious symbols carved on the walls. Given its apparent age, he regarded this as the palace of King Minos, but located the Labyrinth in a nearby cave at Ayia Irini. This too was an ancient quarry, and shows Kalokairinos’s faith in the later literary traditions.
Kalokairinos’s discovery rapidly attracted the attention of foreign archaeologists. They agreed that the building looked ancient but went a step further than Kalokairinos and identified it with the Labyrinth. William Stillman sent a report to the Archaeological Institute of America describing the building with its complicated corridors as the 'Daedalian Labyrinth'.
Kalokairinos had been forced to stop his excavations by the Cretan authorities because at that time Crete was part of the Ottoman Empire and it was feared that his finds would be removed to the museum at Constantinople.
EXCAVATING THE LABYRINTH
When Arthur Evans visited Knossos in March 1894, he was shown round the excavations by Kalokairinos and wrote in his diary, 'I see no reason for not thinking that the mysterious complication of passages is the Labyrinth'.
He was fascinated by the symbols carved on the walls, including a sign in the shape of a double axe. By purchasing a part of the land and waiting until Cretan Independence, Evans was able to establish the rights to excavate.

Sir Arthur Evans at the Palace of Knossos excavations, 1901, GB1648
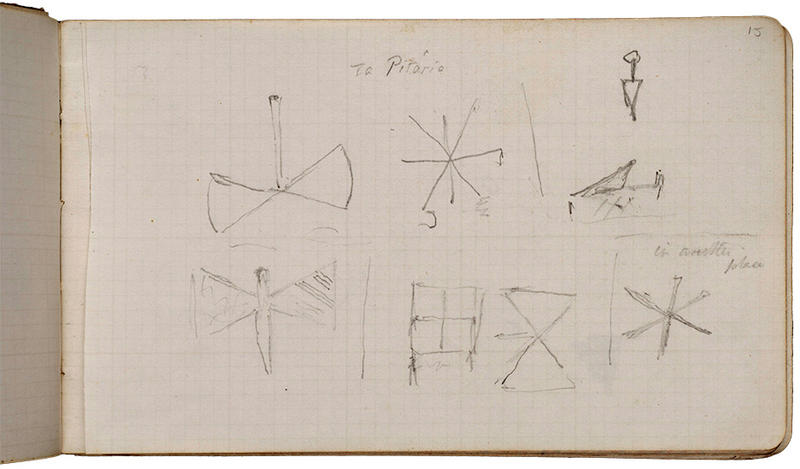
Evans' notebook with drawings of Knossos masons’ marks and the double axe shape. AJE/1/2/1/6. Both © Ashmolean Museum
Evans uncovered the rest of the labyrinthine building he called ‘the Palace of Minos’ between 1900 and 1904.

Annotated ground plan of ‘The Palace of Minos’ in 1903. Ashmolean AJE/4/2/1/1/1
A number of discoveries convinced him that this was indeed the Labyrinth including frescoes of people leaping over bulls which echoed the myth of the Minotaur.
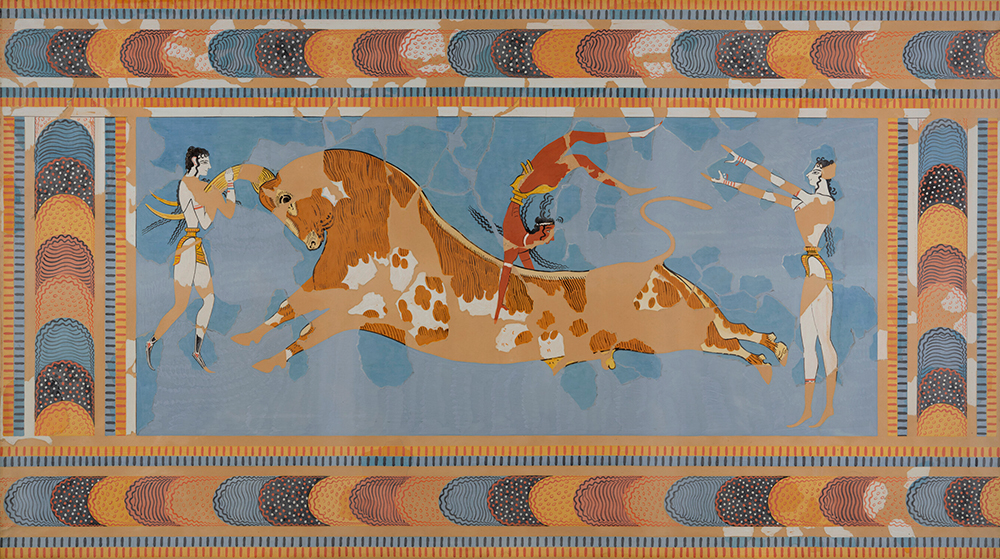

Restoration drawing of the ‘Taureador Fresco’ from Knossos, 1902 © Ashmolean Museum
He found further carvings of double axes and suggested that since an ancient name for this symbol was ‘labrys’, labyrinth must mean ‘House of the Double Axes’.
In other words, the Palace at Knossos and the Cretan Labyrinth were one and the same.
REBUILDING THE LABYRINTH
Almost immediately, Evans and his team set about restoring, and then rebuilding, this Bronze Age building, now thought to have existed from 2000–1350 BCE.
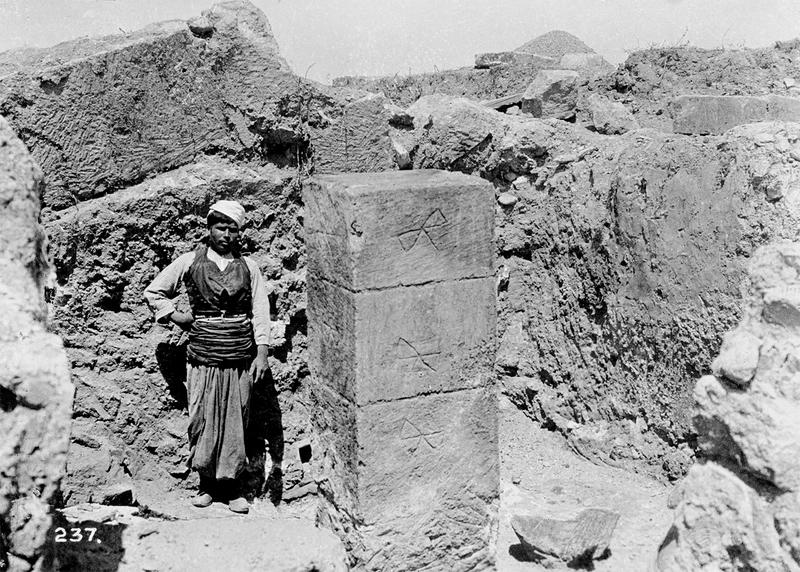

Cretan worker next to a pillar in Knossos Palace (West Pillar Crypt), 1900 © Ashmolean Museum
Some of the later ‘reconstitutions’ as he called them, used reinforced concrete to promote his theories. The reconstructed bull fresco at the North Entrance, he suggested, had continued to stand even after the Palace had been destroyed, inspiring the myth of the Minotaur and the Labyrinth.
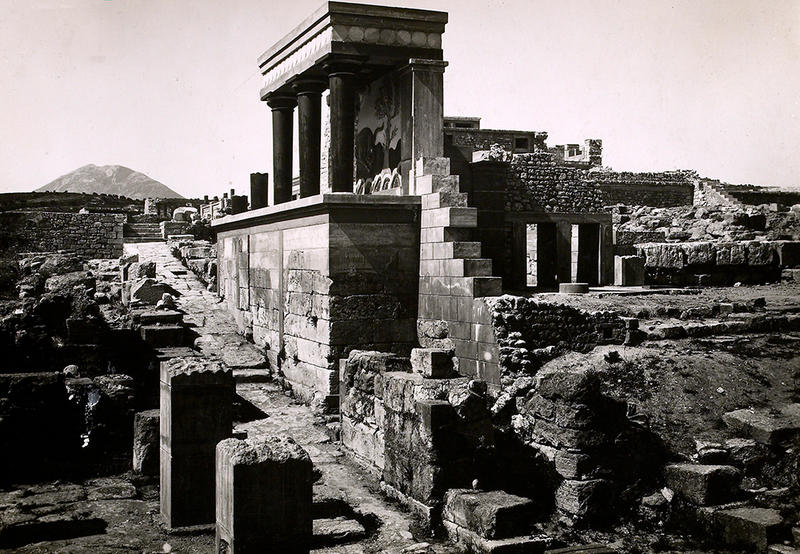

The restored North Entrance at Knossos, c. 1930 © Ashmolean Museum
Among those inspired by Evans’s reconstructions have been the designers of the game Assassin’s Creed Odyssey. Their version of the Palace of Minos, with its underground labyrinth, is the latest retelling of the myth in the exhibition Labyrinth: Knossos, Myth and Reality.
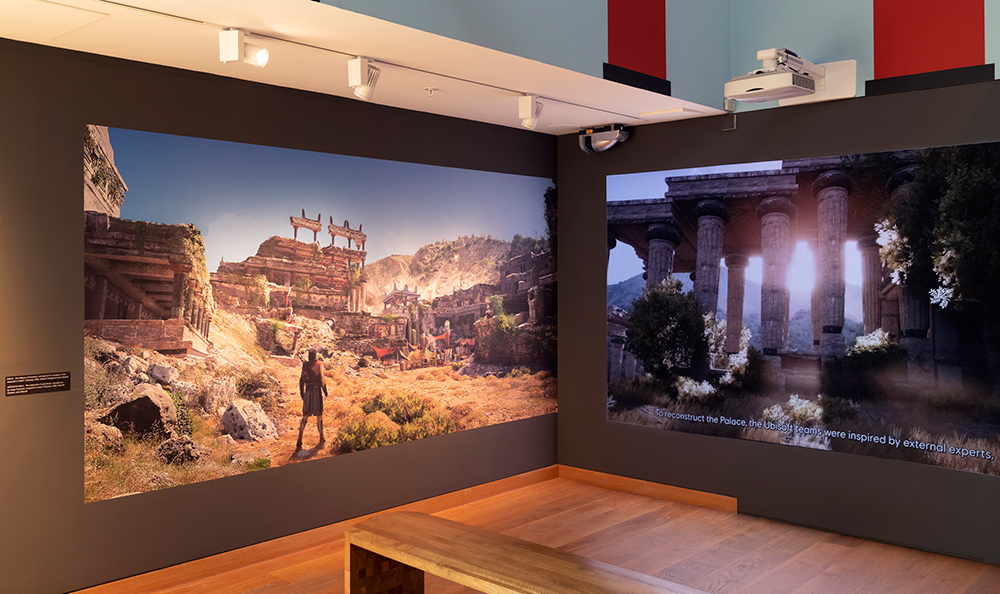

Ubisoft's special video installation of the Palace and Minotaur experience in the Assasin's Creed Odyssey game, showing in the Labyrinth exhibition
By bringing the game together with Greek vases, early modern maps and Bronze Age finds from Knossos, the exhibition shows how the myth of the Labyrinth continues to develop.